Operculectomy
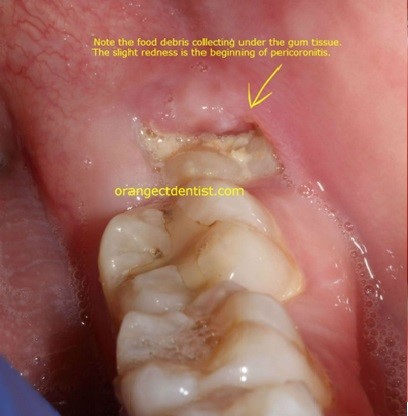
Operculectomy is a minor surgical procedure involving the removal of the operculum, a flap of gum tissue that covers a partially erupted tooth, most commonly a wisdom tooth (third molar). This procedure is often performed to alleviate pain, reduce the risk of infection, and resolve issues caused by food and bacteria trapped under the gum flap.
Indications for Operculectomy:
Pericoronitis: Inflammation and infection of the gum tissue surrounding a partially erupted tooth.
Recurrent Infection: Frequent infections in the gum tissue around the tooth.
Pain and Discomfort: Persistent pain due to pressure and irritation caused by the operculum.
Difficulty in Cleaning: Difficulty maintaining oral hygiene around the partially erupted tooth, leading to decay or gum disease.
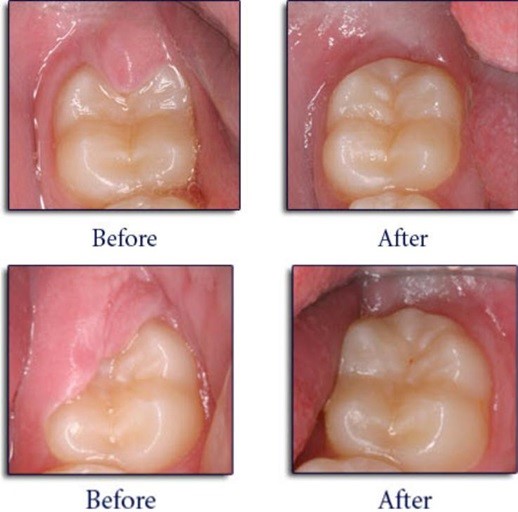
Procedure:
1. Preparation: The area is typically numbed with a local anesthetic to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
2. Incision and Removal: The dentist or oral surgeon makes a small incision in the gum tissue to remove the operculum. This may be done using a scalpel, laser, or electrocautery device.
3. Cleaning: The area is thoroughly cleaned to remove any debris and reduce the risk of infection.
4. Stitches: In some cases, stitches may be used to close the incision and promote healing, though often the wound is left to heal on its own.
Post-Operative Care:
Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications to manage pain.
Oral Hygiene: Gentle brushing and rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash to keep the area clean.
Diet: Soft foods and avoiding chewing near the surgical site to prevent irritation.
Follow-Up: A follow-up visit may be required to ensure proper healing.
Risks and Complications:
Infection: There's a risk of infection at the surgical site, which can be managed with antibiotics.
Bleeding: Some bleeding is normal, but excessive bleeding should be reported to the dentist.
Swelling and Bruising: Mild swelling and bruising are common and typically subside within a few days.
Recurrence: In some cases, the gum tissue may regrow, necessitating another procedure.
If you suspect you might need an operculectomy, consult with your dentist or oral surgeon to discuss your symptoms and determine the best course of action.