Sensitivity
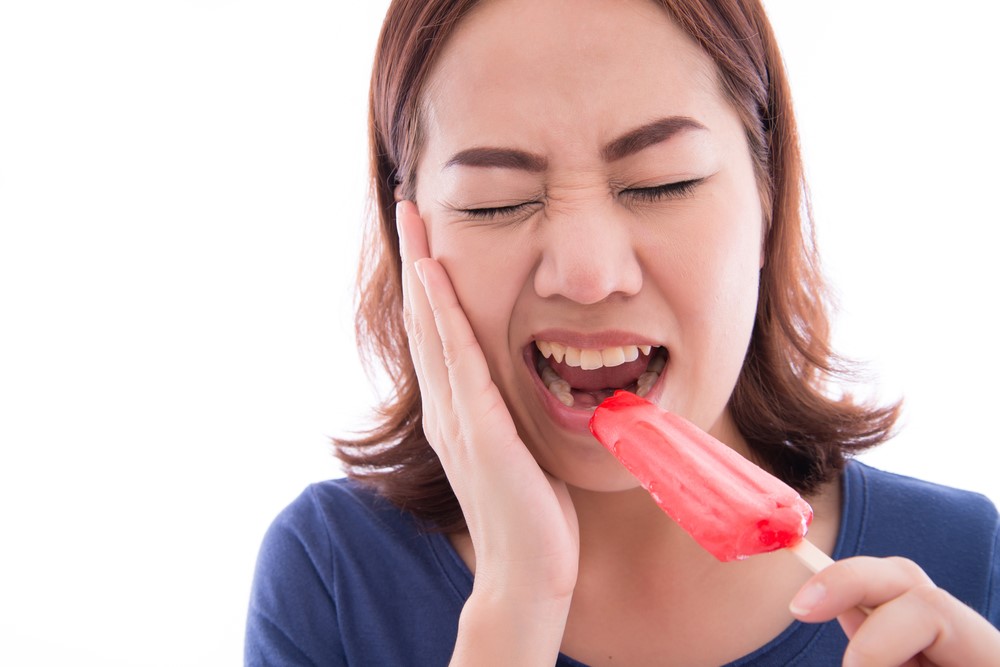

Tooth sensitivity, often referred to as dentin hypersensitivity, is a common Dental problem characterized by discomfort or pain in teeth when exposed to certain stimuli, such as hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. This condition can also occur during brushing or flossing.
What Causes Tooth Sensitivity?
Tooth sensitivity can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
1. Worn Enamel: The enamel is the outer protective layer of your teeth. Over time, it can wear down due to:
- Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush.
- Consuming acidic foods and beverages.
- Teeth grinding (bruxism).
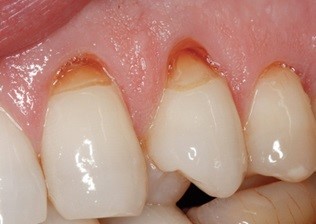
2. Gum Recession: When gums recede, the underlying dentin is exposed, leading to sensitivity.
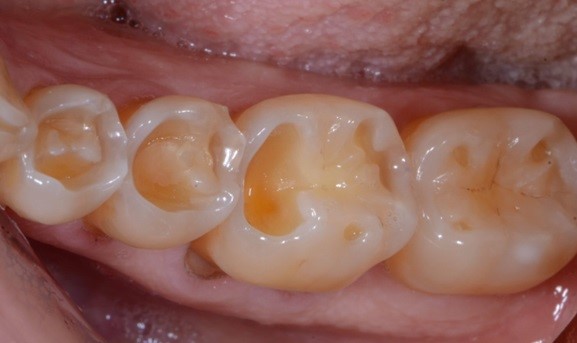
3. Tooth Decay and Damage: Cavities, cracks, or chips in teeth can expose the dentin and cause sensitivity.
4. Dental Procedures: Sensitivity can occur after certain Dental treatments, such as teeth whitening, fillings, or crowns.
5. Gum Disease: Inflammation and infection of the gums (gingivitis or periodontitis) can lead to gum recession and exposure of tooth roots.
Symptoms of Tooth Sensitivity
Common symptoms include sharp, sudden pain when teeth are exposed to:
- Cold air or drinks
- Hot drinks or foods
- Sweet or acidic foods and beverages
- Brushing and flossing
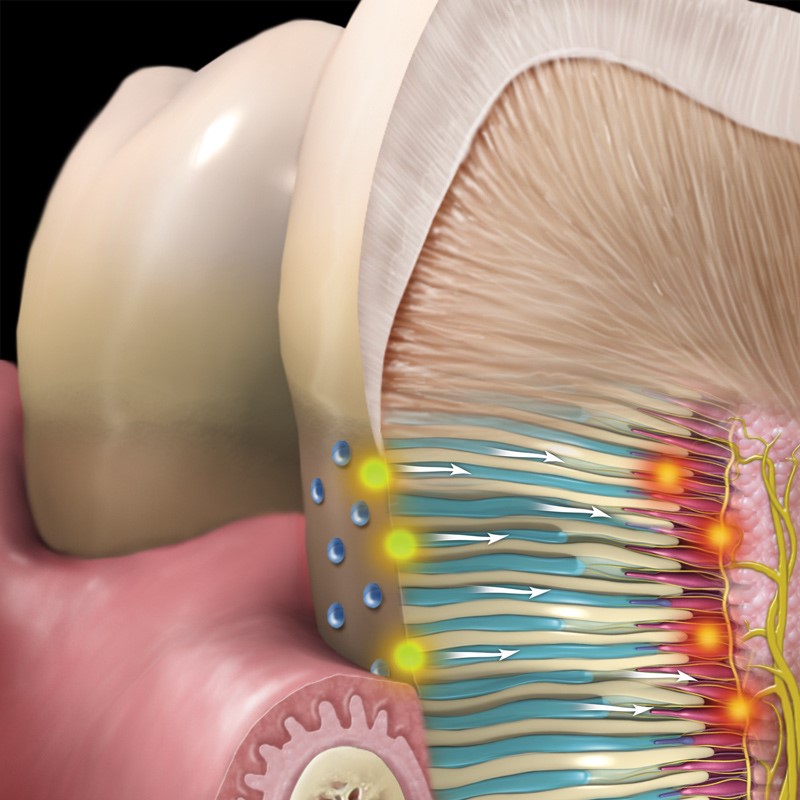
There are several ways to manage and reduce tooth sensitivity:
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Brush gently and avoid aggressive scrubbing.
- Desensitizing Toothpaste: Specially formulated toothpaste can help block pain signals from the tooth surface to the nerve.
- Fluoride Treatment: Your dentist may apply fluoride gel or varnish to strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity.
- Avoid Acidic Foods and Drinks: Limit consumption of acidic items like citrus fruits, soda, and wine.
- Use a Mouthguard: If you grind your teeth, a mouthguard can protect your teeth from further damage.
- Professional Dental Care: Regular Dental check-ups and cleanings can help prevent and manage sensitivity. Your dentist can also recommend treatments tailored to your specific needs.
When to See a Dentist
If tooth sensitivity persists or worsens, it’s important to consult with a dentist. Persistent sensitivity can indicate more serious issues like cavities, gum disease, or significant enamel erosion that require professional intervention.
Preventing Tooth Sensitivity
To prevent tooth sensitivity:
- Maintain good oral hygiene habits.
- Use a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth.
- Avoid overly aggressive brushing.
- Limit intake of acidic and sugary foods and drinks.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
Conclusion
Tooth sensitivity can be a painful and bothersome issue, but with proper care and management, it can be alleviated. If you experience persistent sensitivity, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice from your dentist. Taking proactive steps can help protect your teeth and maintain a healthy, pain-free smile.